Welcome to DU!
The truly grassroots left-of-center political community where regular people, not algorithms, drive the discussions and set the standards.
Join the community:
Create a free account
Support DU (and get rid of ads!):
Become a Star Member
Latest Breaking News
Editorials & Other Articles
General Discussion
The DU Lounge
All Forums
Issue Forums
Culture Forums
Alliance Forums
Region Forums
Support Forums
Help & Search
Environment & Energy
Related: About this forumHow hot can Earth get? Our planet's climate history holds clues
By Elise Cutts
JULY 17, 2025 AT 9:00 AM
Our species likes it cold.
Homo sapiens evolved in — and still inhabits — one of Earth’s rare and fragile ice ages, periods distinguished not by an abundance of saber-toothed cats and woolly mammoths but by ice caps at the poles. For most of its 4.5-billion-year history, our planet was too warm for polar ice. Tyrannosaurus rex’s steamy Cretaceous kingdom 66 million years ago was in many ways a more representative slice of history than our own. Back then, reefs blanketed the beds of shallow seas as warm as bathwater, and jungle creatures watched the southern lights dance behind gaps in the thick canopies of Antarctic rainforests.
--more--
https://www.sciencenews.org/article/climate-change-history-earth-warming
JULY 17, 2025 AT 9:00 AM
Our species likes it cold.
Homo sapiens evolved in — and still inhabits — one of Earth’s rare and fragile ice ages, periods distinguished not by an abundance of saber-toothed cats and woolly mammoths but by ice caps at the poles. For most of its 4.5-billion-year history, our planet was too warm for polar ice. Tyrannosaurus rex’s steamy Cretaceous kingdom 66 million years ago was in many ways a more representative slice of history than our own. Back then, reefs blanketed the beds of shallow seas as warm as bathwater, and jungle creatures watched the southern lights dance behind gaps in the thick canopies of Antarctic rainforests.
--more--
https://www.sciencenews.org/article/climate-change-history-earth-warming
This is an excellent deep dive into geologic time and what the past might tell us about the future.
What folly it was to trash the unique environment we humans evolved in, but no worries, our fossil fueled civilization is unsustainable and will be gone, from the perspective of geological time, in a blink of an eye.
2 replies
 = new reply since forum marked as read
Highlight:
NoneDon't highlight anything
5 newestHighlight 5 most recent replies
= new reply since forum marked as read
Highlight:
NoneDon't highlight anything
5 newestHighlight 5 most recent replies
How hot can Earth get? Our planet's climate history holds clues (Original Post)
hunter
Jul 2025
OP
Caribbeans
(1,285 posts)1. WAPO 09/2024
Scientists have captured Earth’s climate over the last 485 million years. Here’s the surprising place we stand now.
An effort to understand Earth’s past climates uncovered a history of wild temperature shifts and offered a warning on the consequences of human-caused warming.
Sarah Kaplan, Simon Ducroquet | Washington Post | September 19, 2024
An ambitious effort to understand the Earth’s climate over the past 485 million years has revealed a history of wild shifts and far hotter temperatures than scientists previously realized — offering a reminder of how much change the planet has already endured and a warning about the unprecedented rate of warming caused by humans.
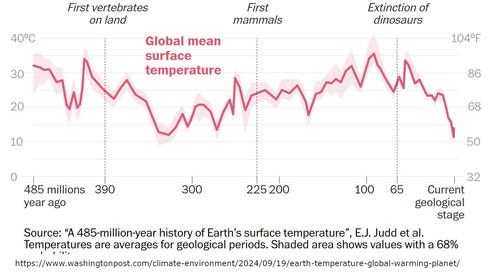
The timeline, published Thursday in the journal Science, is the most rigorous reconstruction of Earth’s past temperatures ever produced, the authors say. Created by combining more than 150,000 pieces of fossil evidence with state-of-the-art climate models, it shows the intimate link between carbon dioxide and global temperatures and reveals that the world was in a much warmer state for most of the history of complex animal life...more
https://archive.ph/vG0CO
https://www.washingtonpost.com/climate-environment/2024/09/19/earth-temperature-global-warming-planet/
An effort to understand Earth’s past climates uncovered a history of wild temperature shifts and offered a warning on the consequences of human-caused warming.
Sarah Kaplan, Simon Ducroquet | Washington Post | September 19, 2024
An ambitious effort to understand the Earth’s climate over the past 485 million years has revealed a history of wild shifts and far hotter temperatures than scientists previously realized — offering a reminder of how much change the planet has already endured and a warning about the unprecedented rate of warming caused by humans.

The timeline, published Thursday in the journal Science, is the most rigorous reconstruction of Earth’s past temperatures ever produced, the authors say. Created by combining more than 150,000 pieces of fossil evidence with state-of-the-art climate models, it shows the intimate link between carbon dioxide and global temperatures and reveals that the world was in a much warmer state for most of the history of complex animal life...more
https://archive.ph/vG0CO
https://www.washingtonpost.com/climate-environment/2024/09/19/earth-temperature-global-warming-planet/
OKIsItJustMe
(21,666 posts)2. Sadly, the effects may be permanent
Recent studies suggest that a “runaway greenhouse effect” similar to the one on Venus is possible.
https://www.earth.com/news/runaway-greenhouse-effect-could-turn-earth-into-an-uninhabitable-hell/
Runaway greenhouse effect could turn Earth into an uninhabitable hell
By Eric Ralls
Earth.com staff writer
A recent study has offered a chilling prognosis for Earth’s future, drawing parallels to the catastrophic scenarios often depicted in Hollywood blockbusters. Researchers have simulated a runaway greenhouse effect, suggesting Earth could soon become an “uninhabitable hell” similar to Venus.
…
Runaway greenhouse effect is irreversible
The study authors point out that while carbon dioxide and methane are known greenhouse gasses, water vapor could be the real trigger for a runaway greenhouse effect on Earth.
As the planet warms due to carbon dioxide and methane emissions, water vapor in the atmosphere, resulting from ocean evaporation, exacerbates the greenhouse effect. This creates a vicious cycle where more evaporation leads to more water vapor, trapping even more heat.
“There is a critical threshold for this amount of water vapor, beyond which the planet cannot cool down anymore. From there, everything gets carried away until the oceans end up getting fully evaporated and the temperature reaches several hundred degrees,” said lead author Guillaume Chaverot, a postdoctoral fellow at UNIGE.
…
By Eric Ralls
Earth.com staff writer
A recent study has offered a chilling prognosis for Earth’s future, drawing parallels to the catastrophic scenarios often depicted in Hollywood blockbusters. Researchers have simulated a runaway greenhouse effect, suggesting Earth could soon become an “uninhabitable hell” similar to Venus.
…
Runaway greenhouse effect is irreversible
The study authors point out that while carbon dioxide and methane are known greenhouse gasses, water vapor could be the real trigger for a runaway greenhouse effect on Earth.
As the planet warms due to carbon dioxide and methane emissions, water vapor in the atmosphere, resulting from ocean evaporation, exacerbates the greenhouse effect. This creates a vicious cycle where more evaporation leads to more water vapor, trapping even more heat.
“There is a critical threshold for this amount of water vapor, beyond which the planet cannot cool down anymore. From there, everything gets carried away until the oceans end up getting fully evaporated and the temperature reaches several hundred degrees,” said lead author Guillaume Chaverot, a postdoctoral fellow at UNIGE.
…
There’s also a problem with the Sun. The Earth may no longer be in the “goldilocks region” because the Sun, has grown warmer since life emerged on Earth; as is natural for a “yellow dwarf,” So, if we succeed in destroying the ecosystem (which looks increasingly likely) it likely won’t come back.
Our planet is being kept cool by the ecosystem itself (i.e. it has been removing greenhouse gases from the atmosphere.) Destroy the cooling mechanisms and…